Introduction
The
focus of this chapter is to explain the BGP Multi-AS Underlay Network design in
BGP EVPN/VXLAN Fabric. It starts by explaining the BGP configuration because
this way explanation can be done by using show and debug command as well as
taking packet captures. The next section discusses of BGP adjacency process and
its related states (Idle, Connect/Active, OpenSent, Open Confirm and Established).
After that, this chapter explains the BGP routing discussing how connected routes
are sent from RIB to Loc-RIB and from there to Adj-RIB-Out (Pre/Post). This section
also introduces how NLRIs received within BGP Update eventually ends up into the
RIB of receiving BGP speaker. In addition, this chapter shortly introduces the MRAI
timer as well as a non-disruptive device maintenance solution. The last section
tries to give an answer which protocol best fits in the Underlay Network of BGP
EVPN fabric.
Infrastructure AS Numbering and IP
Addressing Scheme
The
AS-numbering scheme used in this chapter is the same as what was used in
chapter 1 but instead of using unnumbered interfaces, each inter-switch
interface now has an IP address assigned to it. It is possible to use the Unnumbered
interface also with BGP using IPv6 Link-Local addressing [RFC 5549]. However,
this solution is not supported by all vendors.
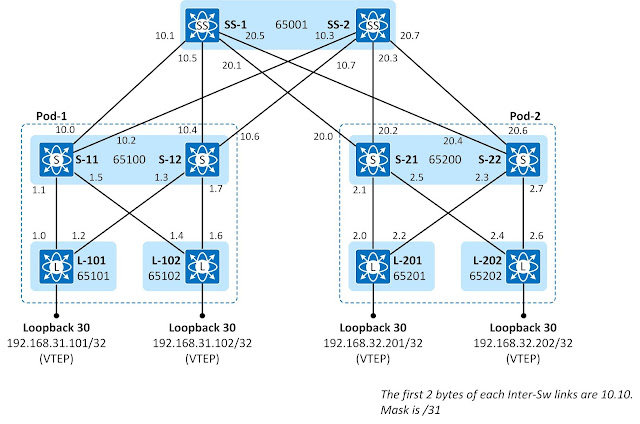
Figure
2-1: IP addressing Scheme.

